
All routes of HPV infection

important! The absence of external signs of HPV does not guarantee that an infected person is absolutely safe from his or her intimate circle.
Infection through household contact
- Ordinary tactile contact, such as a hug or handshake. The likelihood of contracting HPV increases if there is damage to the skin (even a small cut, scrape, or scratch can be enough to allow infection to penetrate a healthy body);
- Use the patient's personal belongings. Virus particles can survive for a long time on daily items such as bedding, towels, underwear, and bath towels;
- While kissing. HPV DNA is present not only on epithelial cells but also in all biological fluids of an infected person and can therefore be transmitted through saliva during kissing.
Sexual transmission of viruses
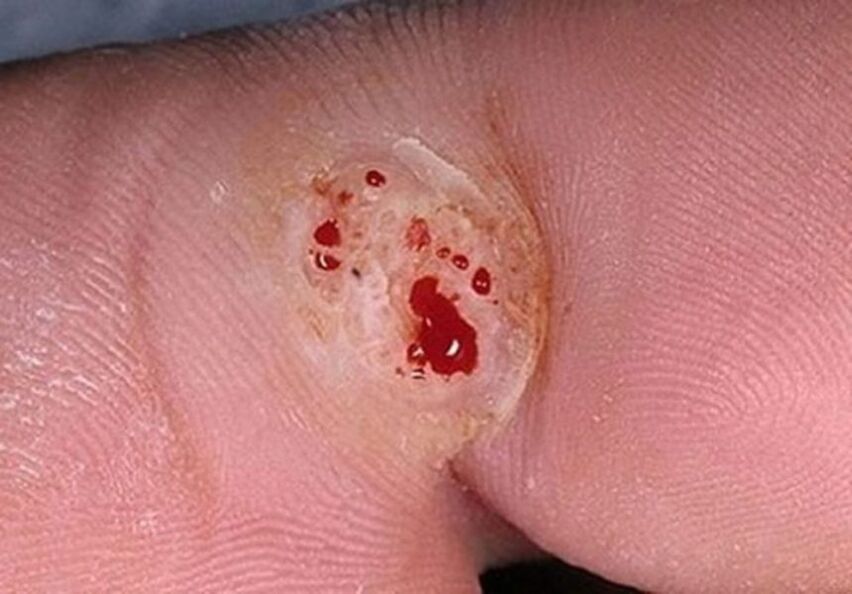
- First, papillary rashes can appear not only on the genitals, but also on the groin and anus. Therefore, the virus is easily transmitted from one partner to another upon contact with unprotected parts of the body;
- Secondly, the latex that condoms are made from has fairly large pores. Viral particles can penetrate them unhindered.
Vertical infection (mother-infant)

autoinoculation infection method
When and what triggers HPV activation
- Have recently suffered from any infectious disease;
- long-term use of oral contraceptives;
- Uncontrolled use of cytostatic drugs (suppression of the immune system);
- Endocrine system dysfunction;
- Pathological conditions of the gastrointestinal tract, especially intestinal flora imbalance;
- Psychological and emotional disorders related to frequent stress, tension, and fatigue;
- helminth infection;
- Frequently suffer from inflammatory skin diseases;
- Whether there are bad habits (smoking, drinking, drug use).
important! Anything that reduces the effectiveness of the body's immune system can lead to HPV activation.
Papillomavirus Treatment
- Suppressing viral activity (returning it to a latent state) by taking antiviral drugs;
- Improving the patient's immune status through the use of interferon drugs;
- Use minimally invasive hardware techniques to destroy pathological tumors;
- Cytostatic drugs (they disrupt the division process of atypical cells) are prescribed when the likelihood of a papilloma becoming malignant is high.

- Tablets (oral);
- Gels, ointments (external use);
- injection(injection);
- Suppositories (rectal suppositories).
- electrocoagulation– Use electric current to cauterize the growth. The procedure is painful and can leave significant scarring;
- cryotherapy– Papillomas freeze under the influence of liquid nitrogen and leave no trace, but this procedure is recommended for removal of small superficial tumors;
- laser destruction– Suitable for removal of superficial and deep papilloma, good cosmetic effect allows use in open parts of the body;
- radio wave technology– Contactless removal of growths with short recovery period and no marks or scars after the intervention.















