Papilloma is the growth on the skin.They can appear anywhere in the human body.It can be the neck, armpit, nasal mucosa, eyelids, or genitals.Unfortunately, these unattractive levels are not experienced by themselves, and over time, these constructs will even become more numerous.
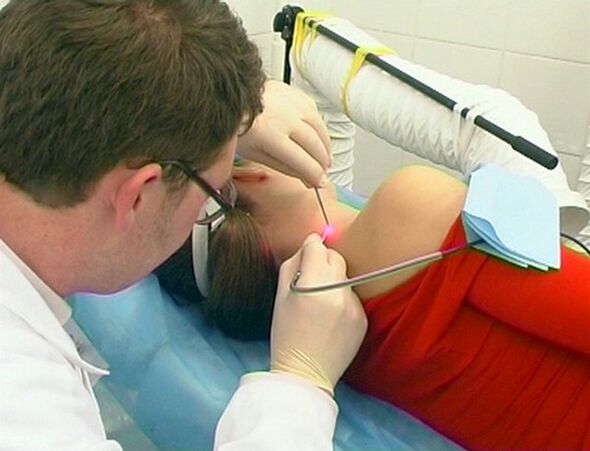
Delete nipple laser
The effect of laser on papilloma is an effective way to eliminate foreign formation.After laser processing of the skin, there is no scar, the surgery will not cause pain and does not require extended recovery.Surgeons often recommend laser treatment, saying this method is to eliminate papillomas, which is not only simple but also safe.After the operation, the beauty of the skin was restored.Believe that such a promise is worth it, or is it just an advertising move?Is laser an advantage over other methods of eliminating papillomas?How does the conversation flow and does the scar remain on the skin?
How do papillomas appear and why do you need to get rid of them?
Papillomas occur when HPV penetrates into the body and is formed benignly.HPV enters the body by sexual contact or family contact.It can penetrate wounds on injured skin or mucous membranes.However, because antibodies and class protect us from influence, this is not particularly dangerous.However, when the body's defense ability weakens, the virus is activated and trapped in "attack".This causes violation of antibodies:
- pregnancy period;
- recurrence of chronic diseases;
- Intestinal diseases, malnutrition;
- Injury and serious forms of disease;
- Bad habits and unhealthy lifestyles;
- Reduce body protection function;
- Unfavorable working conditions.
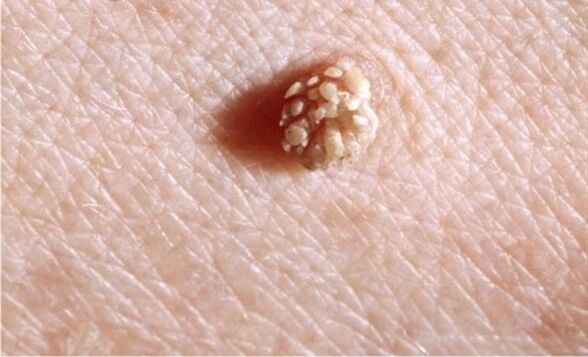
There are more than one hundred papillomaviruses, and each education has a different structure and structure.Such benign formation can usually cause trouble.
- If growths appear in open areas of the body, they can damage the appearance and often cause inferiority to the owner.Injection of formations can cause their growth and infection.
- Papillomas in closed areas of the body may be damaged by objects in clothing.Injection of formations can cause their growth and infection.
- The influence of harmful factors can lead to the distress of the tumor.This happens rarely, but this risk should not be ignored.Papillomas on the sexual genitals are particularly at risk of rebirth.In addition, they interfere with important functions such as urination, sexual contact and bowel movements.Papillomas can degenerate into malignant tumors
- Growing growth is located on the mucus surface of the respiratory system and can cause respiratory disorders and even athletes.
To summarize the above, it should be noted that such formations must be eliminated on the organ or epidermal surface tissue, not only to address aesthetic characteristics, but also to minimize the possibility of developing dangerous diseases.
Positive and negative aspects of the process
In a cosmetic surgeon's cosmetic clinic or office, several methods can be provided for eliminating papillomas: radio waves, surgical removal or burning with nitrogen.However, the use of lasers has many important advantages.

- Low levels of trauma.High-quality equipment affects only the problem area, not the healthy area and mucosa.During the operation, there are spikes of injured blood vessels, which can prevent bleeding.The wounds of papillomas are small and neat, and there is no trace of scars or scar forms.
- Infertility.The impact of lasers eliminates the possibility of infection in processing areas.
- Papillomas can be eliminated in large groups even in difficult-to-access places as well as in risk areas, genitals, face and mucosa.Laser removal of papillomas has many advantages.
defect.
- With the laser effect, the papilloma completely evaporates, so histology will not work in the future.Therefore, if growing malignant tumors are suspected, it is impossible to use laser.Previously, laboratory tests such as dermatoscopes, histology and biopsy were necessary to ensure benign tumors.If you have an oncological disease, then only the surgeon who is addressed by an oncologist can remove the papilloma.One of the disadvantages of this papilloma removal method is that histological analysis is not always possible
- High program costs.The laser method of removing the strata is more expensive than when using other methods.But the price is still affordable, especially because this method allows you to eliminate growth without actually leaving traces on the skin or mucous membranes.
Which laser is used for this process?
In modern beauty science, several types of laser devices are used to get rid of growth.Carbon dioxide emits infrared radiation and quickly evaporates tumors.This type of laser exposure is very popular, but it is important - the scars are still there.The shorter waves emitted by ERBIUM lasers have a milder effect and are more effective than carbon dioxide lasers.Pulse lasers have a stronger effect on previous types of lasers that form the cellular structure of their blood cells, resulting in the destruction of oxygen molecules in red blood cells.Therefore, all capillaries are destroyed inside the tumor and are no longer fed.The treatment was not noticed by the patient.There are no scars in the treatment site.
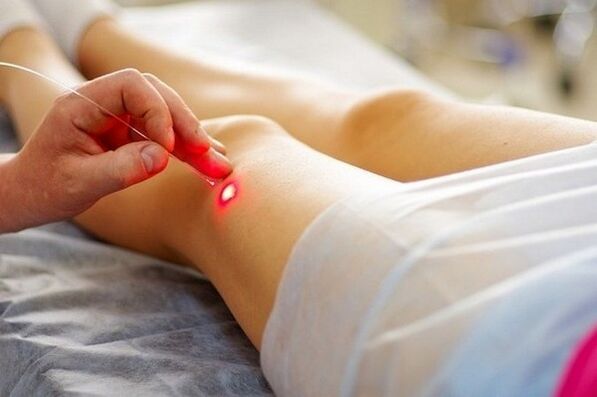
How painful is the surgery?
Laser tumor removal is a non-invasive treatment.It does not cause bleeding and does not harm treated surfaces.This process does not cause pain.To avoid discomfort, local anesthesia is recommended.Pain rarely occurs during recovery after a meeting.Removing tumors on the soles can cause considerable pain.In this case, you need to use pain medication.Due to the severe pain, it is worth taking pain medication.Experts do not recommend discomfort of gels or creams based on corticosteroid medications, as they tighten the healing process.
After the program
After the operation, the experts who conducted the course told the patient what methods they could take care of in the treatment area.In most cases, a dry solution is prescribed: a strong solution of potassium cannabinate.
Proper care of wounds
The duration of the recovery period depends on several reasons: growth and its growth depth, immune status and strict medical advice implementation.During the normal course of the recovery period, traces of growth from small recovered for several days within a few days and after larger - from 2 weeks to 1.5 months.On the first day after the meeting, the skin was congested (red) similar to the consequences of sunburn, and then a shell appeared on the wound area and a small swelling appeared on the nearby tissue.A few days later, the edema disappeared, the shell fell off, and the young skin opened.Even after 2-3 weeks, skin tone is normalized and the surface recovery process of laser end treatment.Usually, within the first 2-3 days, strong traces of the processing site disappear.It's not worth extra treatment or applying the skin in any way without anything healing alone.

If the laser effect is extensive and deep, medical ointments can be developed.Observe the hygiene of the treatment area and do not decorate cosmetics and therapeutic agents if no doctor prescribes it.By laser treatment of genital skin, it is recommended to rule out the possibility of sexual contact until the mucus surface is fully restored or until the doctor eliminates the ban on intimacy.The effect of laser on deep or particularly large growth of the skin leaves small white scars, and pigmentation in the skin area is affected by laser rays and may be changed.There may be almost no obvious scars.Therefore, there is no trace after healing on the skin, the following recommendations must be followed.
- Do not allow the effects of high and low temperatures and wetness in injured areas.During recovery, it is impossible to stay in the sun for a long time, and the debt accepts water flow.
- Don't comb the wounds, don't tear the shells off them.
- Treat the skin with green iodine, place it to compress, etc.
If the growth is located in an open area of the body and is in contact with water frequently, after the shower, dry with a sterile napkin or hair dryer, blowing at the lowest speed at cold air.A place worth drying after shower.It is impossible to remove papillomas with laser light in the following cases:
- Tumor diseases, reduced immunity, diabetes, and recurrence of chronic diseases;
- Pregnant;
- Patients have high sensitivity or allergic reactions to ultraviolet rays.
- exacerbate infection and inflammation processes and diseases;
- If the papilloma is adjacent to a region of the skin infected by bacteria, fungi, or viruses;
- The use of scrubs, activities in the solarium, and the use of cosmetics.
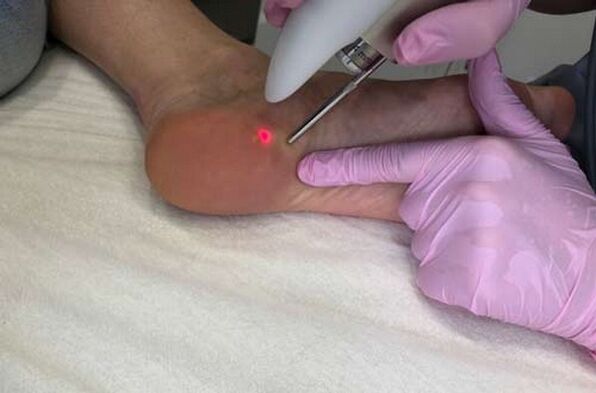
This procedure is contraindicated.Using lasers, it is recommended to remove small tumors from 1 to 5 mm.To get rid of large papillomas, you can use the electrocoagulation method.
Possible complications
Complications and side effects of laser exposure are rarely seen.
- The most common side effect is wound infection during recovery.However, such problems rarely occur because after the process, dry marks are left, which quickly fill up.The patient develops problems when the patient touches the treatment area with unwashed hands.
In rare cases, complications occur
Cost of laser processing meetings
The pricing of the conference will be determined to a greater extent to determine the number of tumors, as well as less localization and size.The clinic sets tariffs, focusing on the papilloma group: from 10 to 10 PCs, from 10 to 20 PCs.etc.Only additional payments are required to eliminate very large growth.Removing large amounts of papillomas will cost less.There is no seasonal discount for this type of program because you can get rid of growth at any time of the year.Since the number of people who want to get rid of papillomas does not decrease, the procedure is inserted into the flow, which means there is no need to stimulate their discount.
Popular issues
Should they say, is the fact that getting rid of warts better in the cold season?
- Yes, in this statement, this makes sense, as solar activity helps the performance of the age point.
If you use laser to remove moles on your head, will it cause hair loss and bald sparks?
- This view is common because laser radiation is used to remove unnecessary vegetation.It should be kept in mind that the device has the target effect achieved using settings.If the purpose of laser exposure is not the hairline, but the skin, it will not cause harm to the hair.After such a hair loss procedure, it will not happen.

- Can moles or papillomas be transferred to minor children?
If the procedure is performed according to the doctor's advice, there is no age limit and there are no contraindications for the child.
- Can I perform the surgery without anesthesia?
This procedure does not require mandatory anesthesia, and the use of anesthesia depends on the patient's pain threshold.Typically, the process takes 5 to 10 minutes and does not cause acute pain.However, the use of anesthesia is desirable.The use of anesthesia is not necessary, but is usually desirable.
- Is it possible to get rid of papillomas on the eyelids or be very close to the eye area?
Yes, such a process is possible.But for some time, edema may appear in the eye area.However, laser has no effect on vision.
- Can I delete the papilloma by myself?
Papillomas are skin defects that cannot be eliminated no matter what!At best, self-assessment of tumors can lead to scars and hematomas, and at worst, bleeding and malignant degeneration.Calls for professional beauticians will avoid infections, complications and other side effects.You cannot delete papilloma by yourself!
- Did the papilloma disappear immediately or after a while after the meeting?
After the operation, the tumor disappeared immediately, leaving a small wound, which was quickly covered by the shell.When it disappears, an area of pink skin will be seen, which blends with the skin's main tones over time.
- Does laser use allow removal of large papillomas?
Yes, this is possible.
- Can I get rid of papillomas on my face?
The use of laser technology allows you to remove skin growth from any area on the skin and even on the mucous membranes - the face is no exception.You can delete this tumor on your face.
Summarize
Laser removal of this tumor is an excellent way to quickly and painlessly eliminate problems.At the same time, you don't have to pay a lot of money for the program.It is important to use all the necessary medications by qualified experts and you don't have to worry about your health.















